
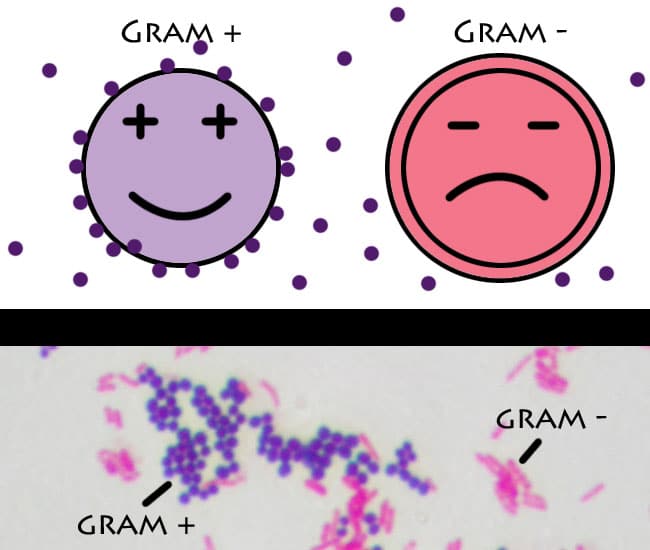
Some of these are lipoteichoic acids, which have a lipid component in the cell membrane that can assist in anchoring the peptidoglycan. Specific to gram-positive bacteria is the presence of teichoic acids in the cell wall. Gram-negative bacteria's S-layer is attached directly to the outer membrane. In gram-positive bacteria, the S-layer is attached to the peptidoglycan layer. Both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria commonly have a surface layer called an S-layer. Also, only some species are flagellates, and when they do have flagella, have only two basal body rings to support them, whereas gram-negative have four. Only some species have a capsule, usually consisting of polysaccharides. A much smaller volume of periplasm than that in gram-negative bacteria.Peptidoglycan chains are cross-linked to form rigid cell walls by a bacterial enzyme DD-transpeptidase.Teichoic acids and lipoids are present, forming lipoteichoic acids, which serve as chelating agents, and also for certain types of adherence.In general, the following characteristics are present in gram-positive bacteria: Their peptidoglycan layer is much thinner and sandwiched between an inner cell membrane and a bacterial outer membrane, causing them to take up the counterstain ( safranin or fuchsine) and appear red or pink.ĭespite their thicker peptidoglycan layer, gram-positive bacteria are more receptive to certain cell wall–targeting antibiotics than gram-negative bacteria, due to the absence of the outer membrane. This is because the thick peptidoglycan layer in the bacterial cell wall retains the stain after it is washed away from the rest of the sample, in the decolorization stage of the test.Ĭonversely, gram-negative bacteria cannot retain the violet stain after the decolorization step alcohol used in this stage degrades the outer membrane of gram-negative cells, making the cell wall more porous and incapable of retaining the crystal violet stain. Gram-positive bacteria take up the crystal violet stain used in the test, and then appear to be purple-coloured when seen through an optical microscope. In bacteriology, gram-positive bacteria are bacteria that give a positive result in the Gram stain test, which is traditionally used to quickly classify bacteria into two broad categories according to their type of cell wall. Gram variable bacteria show a mix of pink and purple cells when stained.Violet-stained gram-positive cocci and pink-stained gram-negative bacilli They can't appear purple after the Gram stain test. acid-fast bacteria are bacteria whose cell walls retain stains particularly well although they aren't closely related to gram positive bacteria. Not all bacteria can be reliably classified through gram staining.Īcid-fast bacteria and gram variable bacteria for example do not respond to gram staining. unfortunately these bacteria also develop resistance more quickly. gram-negative bacteria are more resistant to antibodies because of their impenetrable cell wall. gram-negative bacteria do not retain the dye for two reasons.ġ) They have an outer membrane getting in the way of the crystal violet andĢ) They lack peptidoglycan to retain the stain.Īlthough both gram positive and gram-negative bacteria can be pathogenic. The Gram stain detects peptidoglycan and since gram positive bacteria have a thick multi-layered peptidoglycan layer they retain the crystal violet dye. the reason for these staining differences is due to differences in cell wall structure which is the chief difference between gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria.

However this is not visible when they are dyed with the darker purple color of the crystal violet stain. "note" that gram positive bacteria also pick up the pink color of the counter stain.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
